What Are Opioids?
What are opioids used for?
Opioids are a type of medication prescribed for acute pain (e.g., after surgery, broken bones, and burns) and, sometimes, chronic pain (lasting longer than 3 months).
In addition to treating pain, opioids like methadone and buprenorphine are used to treat opioid use disorder.
Opioids may be prescribed as: |
Some common prescription opioids include: |
|
|
How do opioids work?
Opioids work by blocking pain signals between the brain and the body. They also affect the part of the brain that is responsible for the function of our lungs and wakefulness; therefore, one of the risks associated with opioid use is they can cause our body to stop breathing resulting in an opioid overdose.
How strong are opioids?
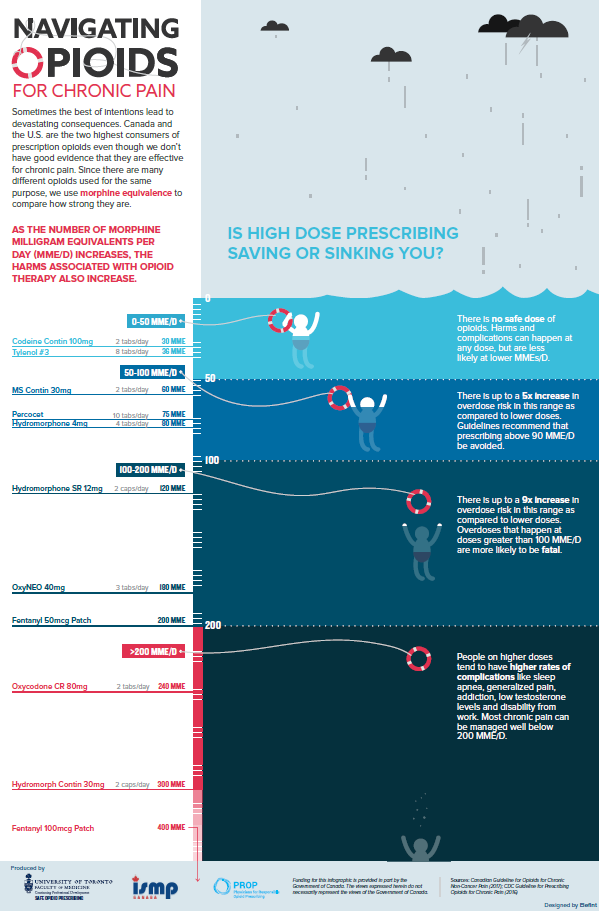
Opioids are powerful pain reducing medications, and each type are different in strength. For example, hydromorphone is five times stronger than morphine.
Your healthcare provider calculates your opioid dosage in Morphine Equivalent Dose (MED or MME), which is a value that shows the strength of an opioid dosage compared to morphine.
MED helps your healthcare provider make safe and appropriate decisions about your daily opioid dosage. To avoid opioid overdose, always make sure to take opioid medications as prescribed for you.
What are side effects of opioids?
Some short-term effects include: |
Some long-term effects include: |
|
|
What is opioid tolerance?
Long-term use of opioids can lead to a reduced response, meaning higher or more frequent doses of an opioid are needed to feel the same effects.
What is opioid dependence?
Using opioids long-term causes the body to adjust its normal functioning around regular opioid use; physical dependence is when the body requires a specific dose of a particular medication in order to prevent withdrawals symptoms. Abruptly reducing or stopping an opioid can cause physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms.
- anxiety, irritability, aggression, restlessness, depression
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- generalized pain
- tremors, sweating, fever
- yawning, running nose, tearing
For many, the concern over withdrawal may be more of a concern than their original pain. If you or your loved ones are concerned with a developing opioid dependence, talk to your healthcare team about reducing your opioid use as it can be done safely and comfortably. See Non-Opioid Treatments For Chronic Pain.