Patient Kidney Health Information
Disclaimer: The information provided in these materials is for educational/information purposes and to assist discussion with your health care team about your medical condition and treatment. It is not medical advice and does not replace advice given by your health care provider.
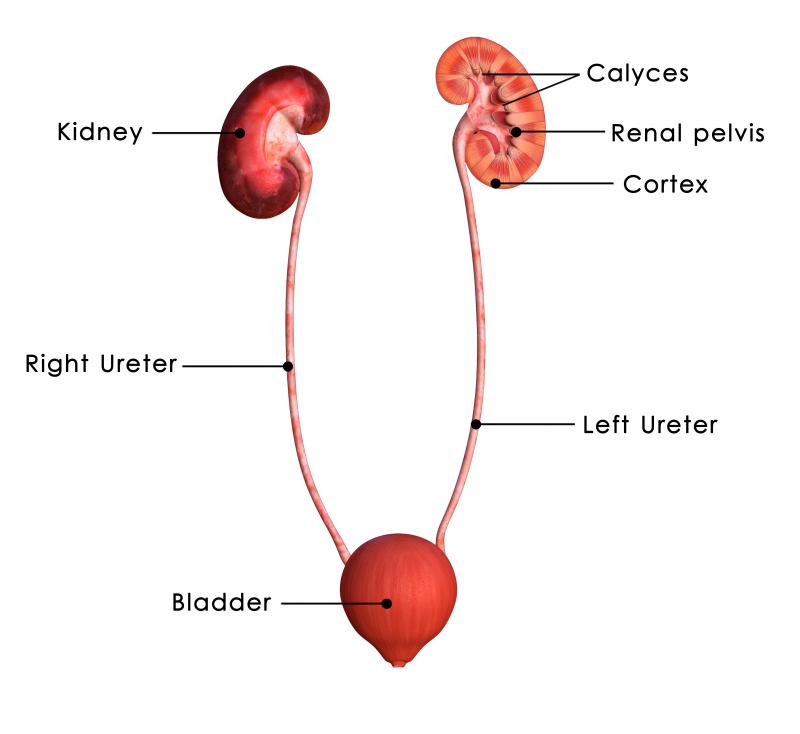
Kidney Health
What do kidneys do?
-
Remove waste products from your body.
-
Remove excess water or retain water if needed.
-
Regulate blood pressure.
-
Ensure safe levels of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphorus.
-
Produce a hormone to help your body make red blood cells.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
-
CKD occurs when kidneys are damaged and not working properly for at least 3 months or more.
-
CKD can range from mild to severe and sometimes leads to kidney failure (called end-stage kidney disease – ESKD)
-
Often more than 70% of total kidney function is lost before people have any symptoms.
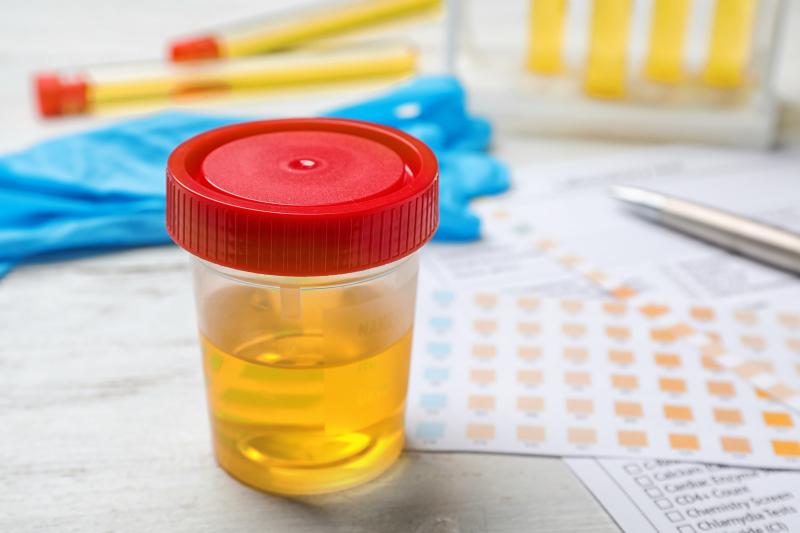
How do you test for Chronic Kidney Disease?
- Two tests are needed to detect kidney damage:
- Blood test to measure serum creatinine.
- Serum creatinine shows us how well the kidneys are removing waste products.
- As serum creatinine increases, kidney function decreases.
- Serum creatinine is used to measure the percentage of kidney function. This is called the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) – the rate at which the kidney removes waste products.
-
Urine test to detect how much albumin or protein is in the urine.
- This test detects damage to the kidney filters and can tell us your risk of losing more kidney function.
- Blood test to measure serum creatinine.
- Sometimes other tests are needed to diagnose kidney disease. These tests include: other blood tests, kidney ultrasound and/or CT scan and MRI or a kidney biopsy.
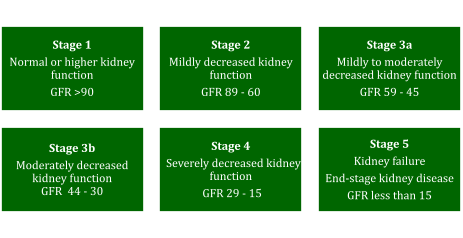
- The amount of damage to your kidneys is grouped into 5 stages.
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
What are the risk factors for Chronic Kidney Disease?
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Family history of kidney disease
- Indigenous, African, Asian, Hispanic descent
- Any history of heart attack, stroke, mini stroke, high cholesterol, gangrene, or limb amputation
- Excessive use of known toxins (such as pain killer and others)
Are you at risk?
- Take the Risk Factor Quiz from the Kidney Foundation of Canada
- This takes about 10 minutes for 10 questions.
- You are able to print your risk assessment so that you can talk with your healthcare provider about getting tested for kidney disease.
Steps to keep your kidneys healthy
- Monitor your blood pressure
- Ask your healthcare provider what your goal blood pressure should be
- Monitor your blood sugar if you have diabetes
- Ask your healthcare provider what your goal blood sugars/A1C should be
- Stop smoking and/or vaping or don’t start
- Limit sodium (salt)
- Excess salt will increase blood pressure and cause swelling
- Ideal sodium intake is 1500 mg/day
- Stay active
- 30 minutes of walking about 5 days per week
- Limit alcohol
- Aim for a healthy body weight
- Take medications as prescribed
- Beware of over-the-counter pain killers or herbal supplements
- Always check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist to be sure they are safe for you
- Get your kidney function tested regularly if you are at risk for kidney disease
- Remember the two tests – blood test for serum creatinine and urine test for albumin/protein.
What are the signs and symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Often more than 70% of total kidney function is lost before people have any symptoms.
- Kidneys cannot remove the waste products very well, so you will notice:
- Tiredness
- Nausea
- No or poor appetite
- Itchiness
- Problems sleeping
- Fuzzy thinking
- Kidneys cannot remove the extra water very well, so you will notice:
- Weight gain
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling, especially in your ankles and legs
- Blood pressure goes up
- Kidneys control blood pressure, so if they do not work well, the blood pressure goes higher and you may have headaches, chest pain, difficulty breathing or more tiredness.
- Kidneys make a hormone to help your body make red blood cells, so if they do not work well, you become low in blood and therefore more tired and have less energy.
- Kidneys regulate minerals (like sodium, potassium, calcium and phosphate), so if they do not work well, you may notice itchiness, joint/muscle pain and irregular heartbeats.