Condition Basics
What is Hodgkin lymphoma?
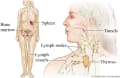
Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer that begins in part of the immune system (the lymph system). White blood cells called lymphocytes can become abnormal or increase in number and grow without control. They may form lumps of tissue called tumours, usually in the lymph nodes of the neck, armpits, or chest.
Like other cancers, Hodgkin can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. To find out how severe your cancer is, your doctor will classify it by type and stage.
Hodgkin is a very curable cancer compared to other cancers. But treatment success depends on your gender, the type of Hodgkin you have, its stage, and your age when you are diagnosed.
What causes it?
Experts don't know what causes Hodgkin lymphoma. But they do know that gene changes (mutations) occur in white blood cells called lymphocytes. These gene changes lead to cancer that affects the immune system and keeps it from working as it should.
Some of the gene changes in Hodgkin lymphoma may be triggered by an abnormal reaction to an infection.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma include swollen lymph nodes, a fever, weight loss, and night sweats.
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask you about your and your family's medical history and will do a physical exam. You may also get:
- Lab tests, including a complete blood count, to check the number of white and red blood cells.
- A biopsy. The doctor may remove part or all of a lymph node to check for cancer. A biopsy is the only sure way to know if you have the cancer.
- A PET scan, a CT scan, or a PET-CT scan.
- Other tests, as needed.
How is Hodgkin lymphoma treated?
Treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma depends on what type of lymphoma you have, the stage of the cancer, and other things, such as your overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Chemotherapy.
This is the main treatment. These medicines kill fast-growing cells, including cancer cells and some normal cells.
- Radiation therapy.
This uses high-dose X-rays to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumours.
- Stem cell transplant.
This replaces damaged cells with healthy stem cells. They help your bone marrow make healthy blood cells.
- Immunotherapy.
This treatment helps your immune system fight cancer. It may be given in several ways.
- Targeted therapy.
These medicines target cancer cells and may cause less harm to normal cells. They help keep cancer from growing or spreading.
Your doctor will talk with you about your options and then make a treatment plan.
Credits
Current as of: October 25, 2024