This is a HealthLine Online content page created by Healthwise. HealthLine Online helps you make better decisions about your health.
Top of the pageCheck Your Symptoms
Leg Problems, Non-Injury
Overview
Minor leg problems, such as sore muscles, are common. Leg problems often occur during sports or recreational activities, work-related tasks, and work or projects around the home. They also can be caused by injuries.
Leg problems may be minor or serious. They may include symptoms such as pain, swelling, cramps, numbness, tingling, weakness, or changes in temperature or colour. Symptoms often develop from exercise, everyday wear and tear, or overuse.
Older adults have a higher risk for leg problems. That's because they lose muscle mass as they age. Children may have leg problems for the same reasons as adults or for reasons specific to children. Problems are often caused by being too active or by the rapid growth of bone and muscle that occurs in children.
It may help you better understand leg problems if you know what the bones of the thigh and lower leg look like, as well as the muscles and tendons. Leg problems that aren't related to a specific injury have many causes.
- Problems can occur when you "overdo" an activity, do the same activity over and over again, or increase your exercise. This may be called an overuse injury, even though you didn't have an actual injury. Examples include bursitis, tendinitis, shin splints, stress fractures, plantar fasciitis, and other muscle strains or tears. Muscle cramps can be caused by activity or dehydration, especially when you exercise in the heat.
- Problems that affect the blood vessels (vascular disease) may include peripheral arterial disease, inflammation of a vein (phlebitis), or a blood clot (thrombophlebitis).
- A blood clot near the surface of the skin may cause only minor problems. But a clot in a deep vein may be more serious. Recent surgery, especially on bones or the pelvic or urinary organs, increases the risk of blood clots, especially in deep leg veins. Prolonged bedrest and inactivity, including sitting or standing in one position for long periods of time, also may increase your risk for blood clots. So can not being able to move a limb for a long time, such as when using a cast or splint.
- Problems affecting the arteries (peripheral arterial disease) can cause cramping pain. It occurs with predictable amounts of exercise, such as walking a short distance, but it improves with rest.
- Other diseases, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus, can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. A transient ischemic attack (TIA) or a stroke can cause numbness, tingling, or loss of function in one or both legs.
Some leg problems are seen only in children, such as swelling at the top of the shin bone (Osgood-Schlatter disease) and swelling and pain in the knee joint (juvenile idiopathic arthritis). Growing pains are common among fast-growing children and teens. Doctors don't know why children have growing pains. These pains often last for 1 or 2 hours at a time and can wake a child from sleep.
Swollen feet are common after you've been sitting or standing for long periods of time or during hot or humid weather. Sitting or lying down and propping up your legs will often relieve this type of swelling. Conditions that put increased pressure on the belly and pelvis, such as obesity and pregnancy, also can cause swelling in the feet and ankles and varicose veins.
- Varicose veins can affect both men and women. They may cause a problem in only one leg.
- The swelling in the feet and ankles that occurs during pregnancy usually gets worse toward the end of the pregnancy and goes away after the baby is born.
Many medicines can cause problems in the legs. For example, birth control pills and other hormones can increase your risk of blood clots. And water pills (diuretics), heart medicines, and cholesterol-lowering medicines (statins) can cause muscle cramps.
Some leg problems only occur at night.
- Restless legs syndrome causes an intense, often irresistible urge to move the legs. This can interrupt sleep and make you overly tired during the day. You may have a "pins-and-needles," prickling, creeping, crawling, tingling, and sometimes painful feeling in your legs. Moving your legs can give you short-term relief.
- Nighttime leg cramps are a sudden tightening (contraction) of the leg muscles in the calf, thigh, or foot. They often occur just as you fall asleep or wake up. They can be painful. These cramps can last from a few seconds to a few minutes. Walking or stretching your leg can sometimes help relieve these cramps.
Most minor leg problems will heal on their own. Home treatment may be all that's needed. But serious leg problems also may occur. They need to be checked by a doctor soon.
Health Tools
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
Check Your Symptoms
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or non-binary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, or natural health products can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
Pain in children 3 years and older
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the child can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain. No one can tolerate severe pain for more than a few hours.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt the child's normal activities and sleep, but the child can tolerate it for hours or days.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The child notices and may complain of the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt his or her sleep or activities.
Symptoms of infection may include:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in or around the area.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Pus draining from the area.
- A fever.
When an area turns blue, very pale, or cold, it can mean that there has been a sudden change in the blood supply to the area. This can be serious.
There are other reasons for colour and temperature changes. Bruises often look blue. A limb may turn blue or pale if you leave it in one position for too long, but its normal colour returns after you move it. What you are looking for is a change in how the area looks (it turns blue or pale) and feels (it becomes cold to the touch), and this change does not go away.
Some medicines can cause leg problems. A few examples are:
- Birth control pills and estrogen. These can increase the risk of blood clots in the leg, which may cause pain or swelling.
- Calcium channel blockers, which are used to treat high blood pressure. These can cause leg swelling.
- Diuretics. These can cause leg cramps.
- Fluoroquinolones. These can increase the risk for tendinitis or tendon rupture.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in adults are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS.
- Long-term alcohol and drug problems.
- Steroid medicines, which may be used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Other medicines used to treat autoimmune disease.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Not having a spleen.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
Make an Appointment
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor. You may need care sooner.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Self-Care
Try the following tips to help relieve minor leg pain, swelling, stiffness, or muscle cramps.
- Remove all jewellery.
Remove rings, anklets, and any other jewellery that goes around a lower extremity. It will be hard to remove the jewellery after swelling starts.
- Rest.
It's important to rest and protect the affected area. Stop, change, or take a break from any activity that may be causing your pain or soreness.
- Use ice.
Put ice or a cold pack on your leg for 10 to 20 minutes at a time. Try to do this every 1 to 2 hours for the next 3 days (when you are awake).
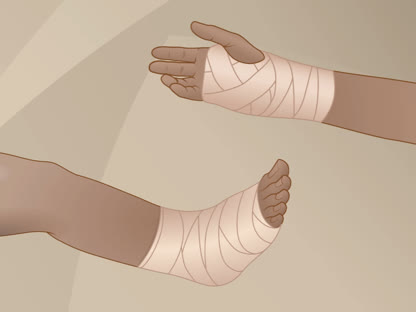
- Wrap the affected area.
Compression, or wrapping the area with an elastic bandage (such as an Ace wrap), will help reduce swelling. Don't wrap it too tightly, because that can cause more swelling below the affected area. Loosen the bandage if it gets too tight. Signs that the bandage is too tight include numbness, tingling, increased pain, coolness, and swelling in the area below the bandage.
- Elevate the affected area.
Try to keep the area at or above the level of your heart to help reduce swelling. Prop up the area on pillows while you apply ice and anytime you sit or lie down.
- Reduce stress on your leg.
- Use a cane or crutch in the hand opposite your painful leg.
- Use two crutches, keeping weight off the leg. You can get canes or crutches from most drugstores. Crutches are recommended if a cane causes you to walk with a limp.
- Avoid more swelling.
For 48 hours, avoid things that might increase swelling. These things include hot showers, hot tubs, hot packs, and drinks that contain alcohol.
- Apply heat.
- After 2 or 3 days, you can try applying heat to the area that hurts. Types of heat therapy include microwavable packs and disposable heating patches.
- Apply heat for 10 to 20 minutes at a time.
- You might also try switching between cold and heat.
- Rub the area.
Gently rub sore or pulled muscles to relieve pain. But don't rub or massage a calf that is swollen.
- Stand and move your legs.
Gentle motion may help with cramps that are brought on by exercise.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
Sports drinks, such as Gatorade, will often help leg cramps.
- Treat your child's growing pains.
If you think that your child is having growing pains, try warmth and massage to relieve discomfort in the legs. Don't rub or massage a calf that is swollen.
- Treat leg cramps.
- Try wearing support stockings during the day. And take frequent rest periods (with your feet up).
- If leg cramps occur during pregnancy, make sure to eat a diet rich in calcium and magnesium. Talk with your doctor about taking a calcium supplement. The doctor may recommend one that doesn't contain phosphorus.
- Don't smoke or use other tobacco products.
Smoking slows healing because it decreases blood supply and delays tissue repair.
If you need to use a wrap, cane, or crutches for more than 48 hours, you may have a more serious injury that needs to be checked by a doctor.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- New or worse pain or swelling.
- New signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, pus, or a fever.
- New or worse numbness, tingling, or cool and pale skin.
- Movement or strength decreases.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Learn more
Watch
Preparing For Your Appointment
You can help your doctor diagnose and treat your condition by being prepared for your appointment.
Credits
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.